Trichoderma: A Green Solution for Agriculture
Introduction
In the realm of agriculture, fungal phytopathogens present a persistent challenge, threatening food security by significantly reducing crop yields. Chemical pesticides have been the go-to solution, but their adverse environmental impacts and the rising resistance among pathogens have driven the search for sustainable alternatives. Enter Trichoderma—a genus of fungi that holds promise not only for biocontrol but also for enhancing plant growth.
The Role of Trichoderma in Agriculture
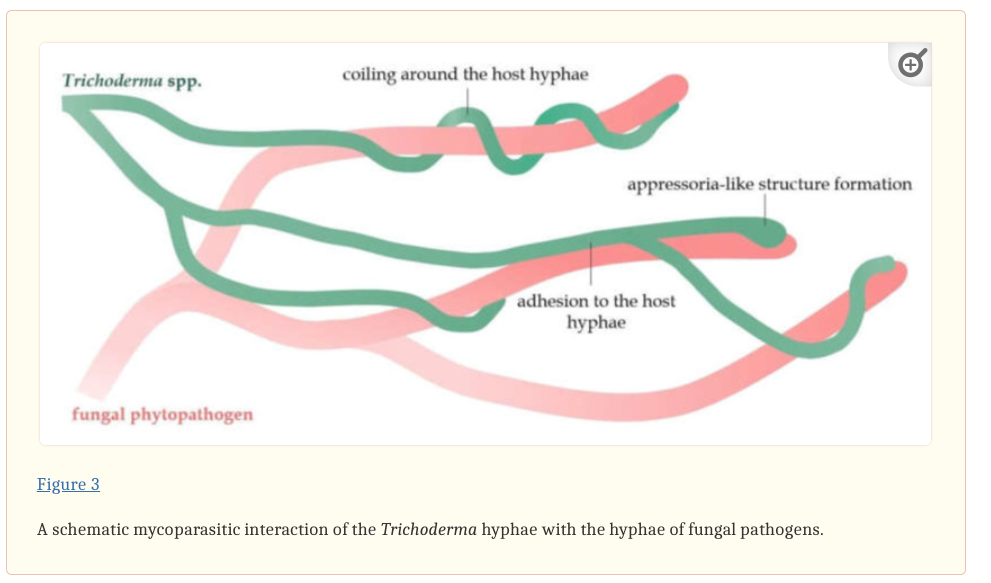
Trichoderma species are dominant components of soil mycobiomes and exhibit an impressive array of beneficial properties. They can colonize plant roots, produce antimicrobial metabolites, and stimulate plant growth through various mechanisms. These fungi operate through complex interactions, including mycoparasitism, competition for resources, and induction of plant resistance, making them effective biological control agents (BCAs).
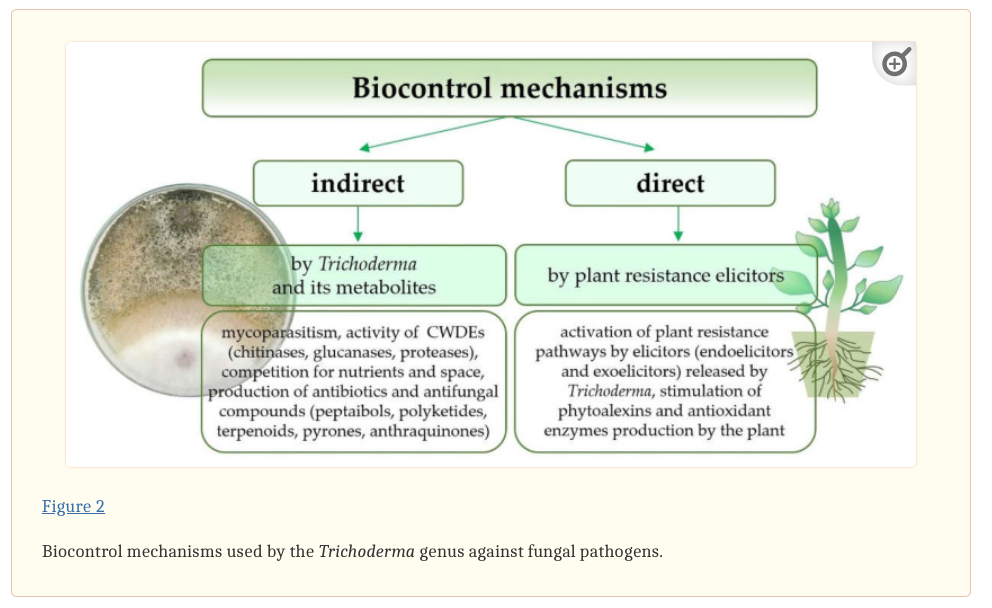
Biocontrol Mechanisms
Trichoderma species employ multiple strategies to combat fungal phytopathogens:
- Mycoparasitism: They parasitize pathogenic fungi, effectively neutralizing them.
- Degradation of Pathogen Cell Walls: Enzymes produced by Trichoderma break down the cell walls of harmful fungi.
- Nutrient and Space Competition: By outcompeting pathogens for essential nutrients and space, they inhibit pathogen growth.
- Induction of Plant Resistance: Trichoderma can trigger a plant’s innate defense mechanisms, enhancing its resistance to diseases.
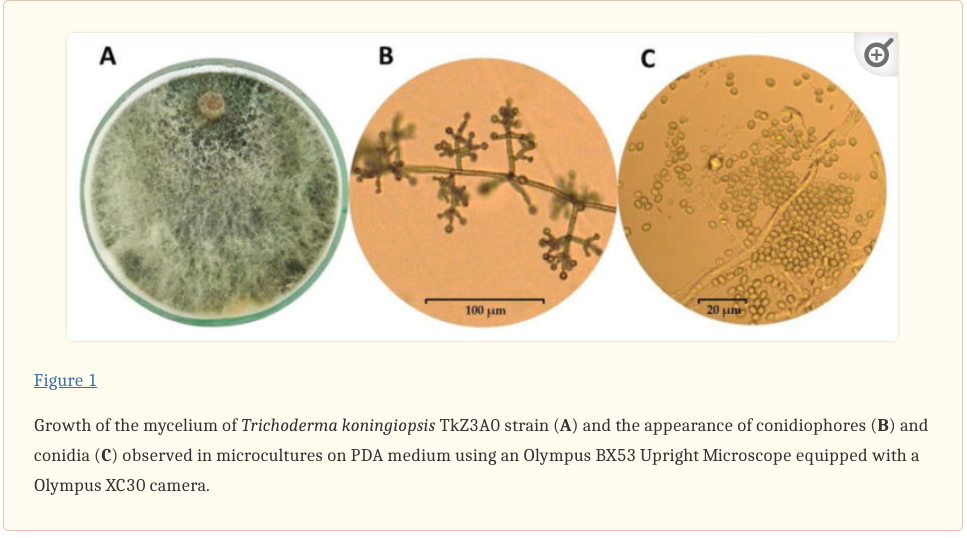
Environmental Adaptability
Trichoderma species are known for their rapid growth, utilization of diverse substrates, and resistance to toxic chemicals, including fungicides and herbicides. This adaptability makes them resilient in various soil ecosystems and climatic conditions.
Applications in Sustainable Agriculture
With the increasing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices, Trichoderma stands out as a viable solution. Its role in biocontrol aligns with Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies and organic farming principles, which seek to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
Biofertilization and Biostimulation
Beyond biocontrol, Trichoderma species also contribute to plant growth promotion. They produce phytohormones and enzymes like ACC deaminase, which enhance nutrient uptake and stress tolerance in plants. This dual functionality positions Trichoderma as a cornerstone in green agriculture, promoting healthier crops and higher yields.
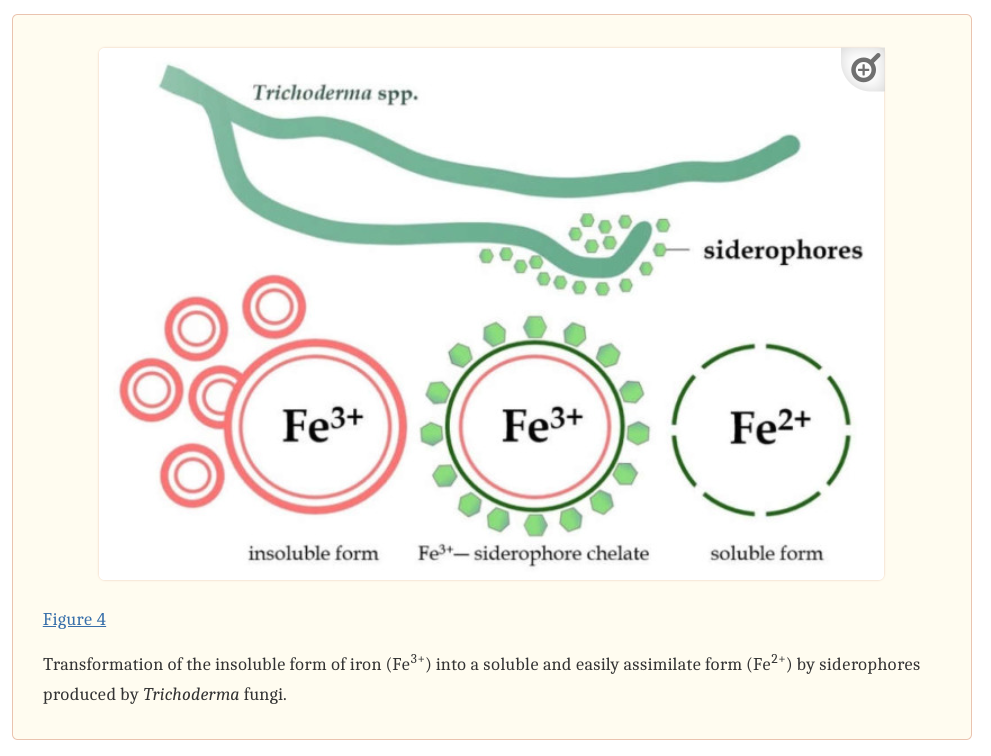
Conclusion
The use of Trichoderma in agriculture represents a significant step towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices. By harnessing the natural capabilities of these fungi, we can reduce the dependency on chemical pesticides, mitigate environmental pollution, and foster robust plant growth. As research and development continue, the potential of Trichoderma in transforming agricultural practices becomes increasingly clear, paving the way for a greener future in farming.